Page 221 - e-Book
P. 221
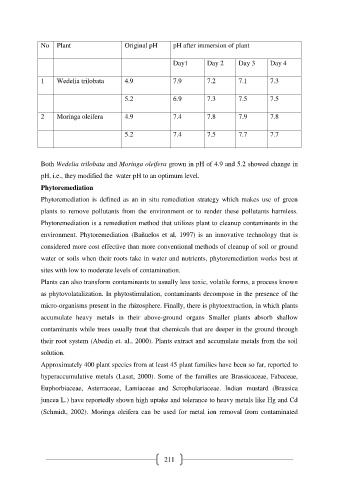
No Plant Original pH pH after immersion of plant
Day1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4
1 Wedelia trilobata 4.9 7.9 7.2 7.1 7.3
5.2 6.9 7.3 7.5 7.5
2 Moringa oleifera 4.9 7.4 7.8 7.9 7.8
5.2 7.4 7.5 7.7 7.7
Both Wedelia trilobata and Moringa oleifera grown in pH of 4.9 and 5.2 showed change in
pH, i.e., they modified the water pH to an optimum level.
Phytoremediation
Phytoremediation is defined as an in situ remediation strategy which makes use of green
plants to remove pollutants from the environment or to render these pollutants harmless.
Phytoremediation is a remediation method that utilizes plant to cleanup contaminants in the
environment. Phytoremediation (Bañuelos et al, 1997) is an innovative technology that is
considered more cost effective than more conventional methods of cleanup of soil or ground
water or soils when their roots take in water and nutrients, phytoremediation works best at
sites with low to moderate levels of contamination.
Plants can also transform contaminants to usually less toxic, volatile forms, a process known
as phytovolatalization. In phytostimulation, contaminants decompose in the presence of the
micro-organisms present in the rhizosphere. Finally, there is phytoextraction, in which plants
accumulate heavy metals in their above-ground organs Smaller plants absorb shallow
contaminants while trees usually treat that chemicals that are deeper in the ground through
their root system (Abedin et. al., 2000). Plants extract and accumulate metals from the soil
solution.
Approximately 400 plant species from at least 45 plant families have been so far, reported to
hyperaccumulative metals (Lasat, 2000). Some of the families are Brassicaceae, Fabaceae,
Euphorbiaceae, Asterraceae, Lamiaceae and Scrophulariaceae. Indian mustard (Brassica
juncea L.) have reportedly shown high uptake and tolerance to heavy metals like Hg and Cd
(Schmidt, 2002). Moringa oleifera can be used for metal ion removal from contaminated
211