Page 531 - e-Book
P. 531
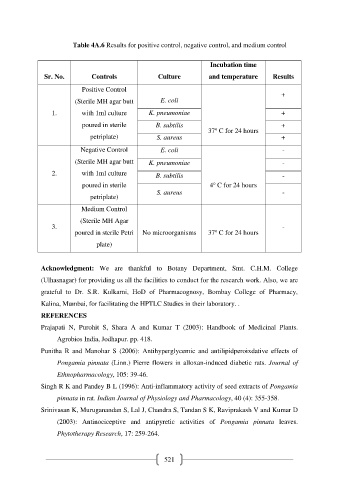
Table 4A.6 Results for positive control, negative control, and medium control
Incubation time
Sr. No. Controls Culture and temperature Results
Positive Control
+
(Sterile MH agar butt E. coli
1. with 1ml culture K. pneumoniae +
poured in sterile B. subtilis +
o
37 C for 24 hours
petriplate) S. aureus +
Negative Control E. coli -
(Sterile MH agar butt K. pneumoniae -
2. with 1ml culture B. subtilis -
o
poured in sterile 4 C for 24 hours
S. aureus -
petriplate)
Medium Control
(Sterile MH Agar
3. -
o
poured in sterile Petri No microorganisms 37 C for 24 hours
plate)
Acknowledgment: We are thankful to Botany Department, Smt. C.H.M. College
(Ulhasnagar) for providing us all the facilities to conduct for the research work. Also, we are
grateful to Dr. S.R. Kulkarni, HoD of Pharmacognosy, Bombay College of Pharmacy,
Kalina, Mumbai, for facilitating the HPTLC Studies in their laboratory. .
REFERENCES
Prajapati N, Purohit S, Shara A and Kumar T (2003): Handbook of Medicinal Plants.
Agrobios India, Jodhapur. pp. 418.
Punitha R and Manohar S (2006): Antihyperglycemic and antilipidperoixdative effects of
Pongamia pinnata (Linn.) Pierre flowers in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Journal of
Ethnopharmacology, 105: 39-46.
Singh R K and Pandey B L (1996): Anti-inflammatory activity of seed extracts of Pongamia
pinnata in rat. Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 40 (4): 355-358.
Srinivasan K, Muruganandan S, Lal J, Chandra S, Tandan S K, Raviprakash V and Kumar D
(2003): Antinociceptive and antipyretic activities of Pongamia pinnata leaves.
Phytotherapy Research, 17: 259-264.
521