Page 527 - e-Book
P. 527
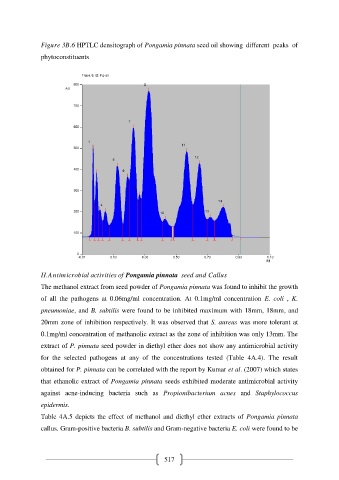
Figure 3B.6 HPTLC densitograph of Pongamia pinnata seed oil showing different peaks of
phytoconstituents
II.Antimicrobial activities of Pongamia pinnata seed and Callus
The methanol extract from seed powder of Pongamia pinnata was found to inhibit the growth
of all the pathogens at 0.06mg/ml concentration. At 0.1mg/ml concentration E. coli , K.
pneumoniae, and B. subtilis were found to be inhibited maximum with 18mm, 18mm, and
20mm zone of inhibition respectively. It was observed that S. aureus was more tolerant at
0.1mg/ml concentration of methanolic extract as the zone of inhibition was only 13mm. The
extract of P. pinnata seed powder in diethyl ether does not show any antimicrobial activity
for the selected pathogens at any of the concentrations tested (Table 4A.4). The result
obtained for P. pinnata can be correlated with the report by Kumar et al. (2007) which states
that ethanolic extract of Pongamia pinnata seeds exhibited moderate antimicrobial activity
against acne-inducing bacteria such as Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus
epidermis.
Table 4A.5 depicts the effect of methanol and diethyl ether extracts of Pongamia pinnata
callus. Gram-positive bacteria B. subtilis and Gram-negative bacteria E. coli were found to be
517