Page 37 - e-Book
P. 37
3.3 Impact on Noise Pollution
Lockdowns has not only shown a significant effect on the quality of air and water but it has
also decreased noise pollution drastically affecting the terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
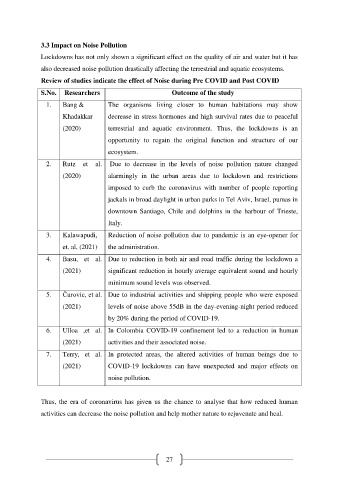
Review of studies indicate the effect of Noise during Pre COVID and Post COVID
S.No. Researchers Outcome of the study
1. Bang & The organisms living closer to human habitations may show
Khadakkar decrease in stress hormones and high survival rates due to peaceful
(2020) terrestrial and aquatic environment. Thus, the lockdowns is an
opportunity to regain the original function and structure of our
ecosystem.
2. Rutz et al. Due to decrease in the levels of noise pollution nature changed
(2020) alarmingly in the urban areas due to lockdown and restrictions
imposed to curb the coronavirus with number of people reporting
jackals in broad daylight in urban parks in Tel Aviv, Israel, pumas in
downtown Santiago, Chile and dolphins in the harbour of Trieste,
Italy.
3. Kalawapudi, Reduction of noise pollution due to pandemic is an eye-opener for
et. al, (2021) the administration.
4. Basu, et al. Due to reduction in both air and road traffic during the lockdown a
(2021) significant reduction in hourly average equivalent sound and hourly
minimum sound levels was observed.
5. Čurovic, et al. Due to industrial activities and shipping people who were exposed
(2021) levels of noise above 55dB in the day-evening-night period reduced
by 20% during the period of COVID-19.
6. Ulloa ,et al. In Colombia COVID-19 confinement led to a reduction in human
(2021) activities and their associated noise.
7. Terry, et al. In protected areas, the altered activities of human beings due to
(2021) COVID-19 lockdowns can have unexpected and major effects on
noise pollution.
Thus, the era of coronavirus has given us the chance to analyse that how reduced human
activities can decrease the noise pollution and help mother nature to rejuvenate and heal.
27